Table of Contents
What Is Leverage?
The Double-Edged Sword Every Trader Must Know
What Is Leverage? We are diving deeper into the world of finance, and with every step, we explore concepts that bring us closer to truly understanding the markets.
In this article, we focus on one of the most crucial terms every trader must learn about: leverage.
Leverage is a powerful financial tool that enables traders to amplify their market exposure by controlling larger positions with a relatively small initial investment. This expanded access can create greater opportunities within the market—but it comes with significant responsibility.
Leverage is not for the faint-hearted. While it has the potential to multiply gains, it can just as easily magnify losses, making it a true double-edged sword. Understanding how leverage works—and more importantly, how to manage the risks it carries—is essential for anyone who wants to navigate the forex market with confidence, discipline, and resilience.
What is Leverage?
Leverage is simply the use of borrowed capital, typically provided by a broker, to increase the size of a trading position beyond the trader’s own invested funds (known as margin). In a more simple term, leverage allows an investor to control a larger position in the market with a smaller initial deposit.
Example:
With 10:1 leverage, a trader who deposits $1,000 can control a position worth $10,000. The broker covers the difference, while requiring the trader to maintain a portion of the trade’s value as collateral (the initial margin).
Leverage acts as a multiplier:
-
If the market moves in your favor, gains are amplified because they are calculated on the full trade value, not just your deposit.
-
If the market moves against you, losses are also magnified, and they can exceed your initial deposit.
Leverage is widely used in:
-
Forex
-
CFDs
-
Stocks
-
Derivatives trading
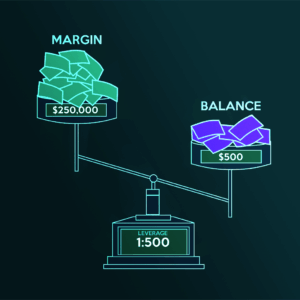
How Does Leverage Work?
Leverage works by using a deposit, known as margin, to provide the trader with increased exposure to an underlying asset. Essentially, you’re putting down a fraction of the full value of your trade, and your broker is loaning you the rest.
Your total exposure compared to your margin is known as the leverage ratio.
Example: EUR/USD Trade
-
Trade size: 1 lot = $100,000
-
Price: EUR/USD at 1.2000
Unleveraged Trade:
-
Margin required: $100,000 (full amount)
-
If price rises by 20 pips → Profit = $200 (0.2% return on capital)
-
If price falls by 20 pips → Loss = $200 (0.2% loss)
Leveraged Trade (10:1):
-
Margin required: $10,000 (10% margin)
-
If price rises by 20 pips → Profit = $200 (2% return on capital)
-
If price falls by 20 pips → Loss = $200 (2% loss)
Comparison Table
| Example | Unleveraged | Leveraged (10:1) |
|---|---|---|
| Trade Size | $100,000 | $100,000 |
| Margin Required | $100,000 | $10,000 |
| Price Movement (+20p) | +$200 → +0.2% | +$200 → +2% |
| Price Movement (-20p) | -$200 → -0.2% | -$200 → -2% |
Pros and Cons of Leverage
Benefits of Leverage for Traders
-
Do More with Less:
Control larger market positions with a smaller initial investment.
-
Boost Potential Returns:
Profits are calculated on the full position size, not just your deposit.
-
Expand Trading Opportunities:
Diversify across forex pairs, stocks, indices, or CFDs.
-
Efficient Use of Capital:
Free up funds for other strategies like hedging or portfolio balancing.
-
Gearing Opportunities:
Use capital more efficiently to commit to multiple trades.
-
Shorting the Market:
Trade rising and falling markets.
-
24-Hour Trading:
Certain markets, such as forex and crypto, are open around the clock.
Risks of Leverage for Traders
-
Magnified Losses:
Losses increase in the same way profits do.
-
Losing More Than Your Deposit:
Especially possible in fast-moving markets.
-
Margin Calls:
Broker may require extra funds if losses reduce your margin.
-
Emotional Pressure:
High leverage can lead to stress and poor decision-making.
-
Market Volatility:
Sudden price swings can wipe out leveraged positions.
-
Funding Charges:
Holding leveraged positions overnight incurs financing costs.
Leverage and Risk Management
- Risk management tools help reduce the downside of leverage:
-
Stop-loss orders:
Close your trade if losses hit a certain level.
-
Take-profit orders:
-
Lock in profits automatically.
-
Price alerts:
Stay updated when assets reach key levels.
-
Diversification & position sizing:
Spread risk and avoid oversized trades.
-
Trading discipline:
Risk only 1–2% of account balance per trade.
-
Trailing & Guaranteed Stop-Losses:
Advanced tools to manage volatility.
What is a Leverage Ratio?
A leverage ratio measures your trade’s total exposure vs. your margin requirement.
Example (with $1,000 deposit):
| Leverage Ratio | Exposure |
|---|---|
| 1:1 | $1,000 |
| 20:1 | $20,000 |
| 50:1 | $50,000 |
The higher the leverage ratio, the larger your market exposure — and the higher both profit potential and risk.
Leverage and Margin in Forex
-
Margin is the amount of money needed to open a leveraged trade.
-
Brokers may require 1% to 5% margin depending on the currency pair and volatility.
-
Margin Calls occur when your account equity falls below the broker’s requirement. If not corrected, positions may be liquidated, locking in losses.
-
Used Margin = funds held to keep positions open.
-
Available Equity = funds left for new trades.
Forex Leverage Calculator
Formula for calculating leverage:
-
L = A / E
-
L = leverage
-
A = asset amount (trade size)
-
E = equity (margin)
-
Or: A = E × L
-
If margin = $1,000 and leverage = 100:1 → Position size = $100,000.
Types of Leverage Ratios
| Margin Requirement | Leverage Ratio |
|---|---|
| 2% | 50:1 |
| 1% | 100:1 |
| 0.5% | 200:1 |
Lower margin requirements = higher leverage, but also higher risk.
Forex vs. Stock Market Leverage
-
Forex: Higher leverage ratios (up to 100:1 or more) due to high liquidity and relatively lower volatility in major pairs.
-
Stocks: Typically 2:1 to 4:1 leverage, as stocks are more volatile and regulations are stricter.
Leverage Beyond Forex
Leverage also exists outside of trading:
-
Operating Leverage: Businesses with high fixed costs see profits (or losses) grow faster as revenue changes.
-
Time Leverage: Delegating tasks or using technology to achieve more in less time.
-
Personal Leverage: Using networks and relationships to unlock new opportunities.
Wrap-Up
Leverage is one of the most powerful tools in forex and financial markets. It allows traders to access larger positions with smaller deposits, creating opportunities to magnify profits. However, it also magnifies losses, and in volatile markets, traders can lose more than their initial investment. The key to using leverage without getting the bad side of it is discipline and risk management: using stop-losses, proper position sizing, diversification, and trading with a clear plan.